Step 1/6

Glossary
Step 2/6

Linear Operators
Step 3/6
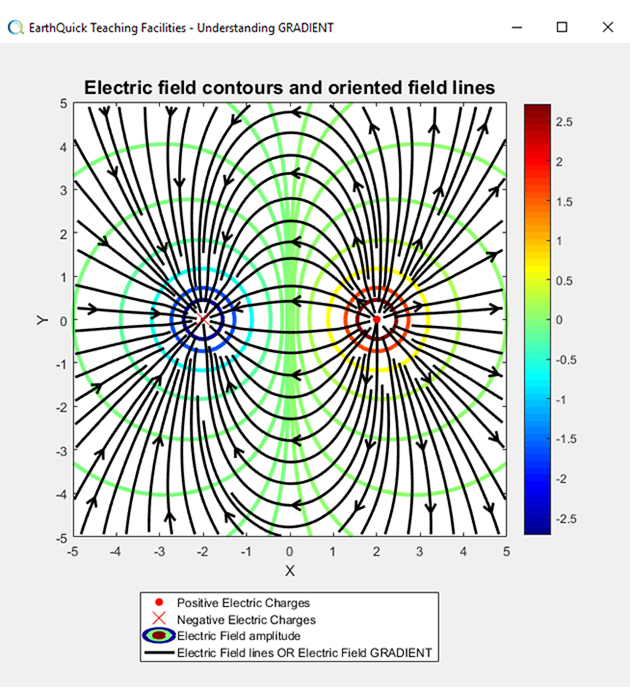
Linear operators in action - Gradient of the electric field amplitude
Step 4/6
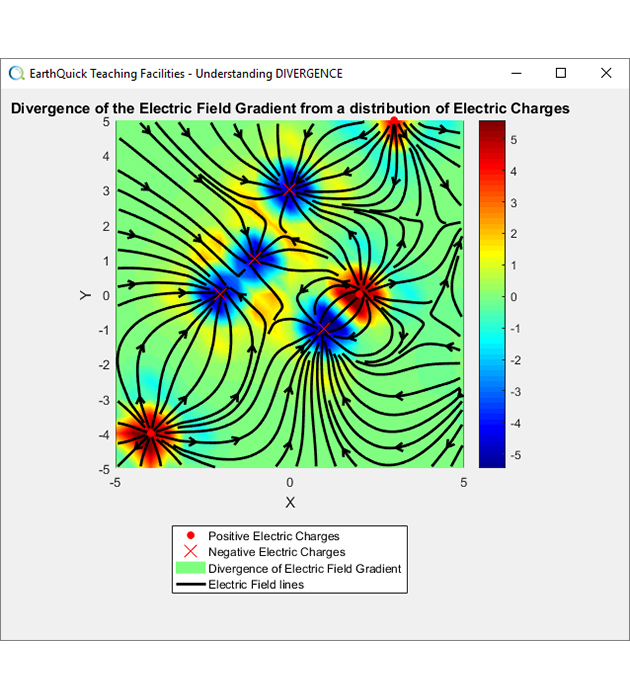
Linear operators in action - Divergence of the electric field amplitude gradient
Step 5/6
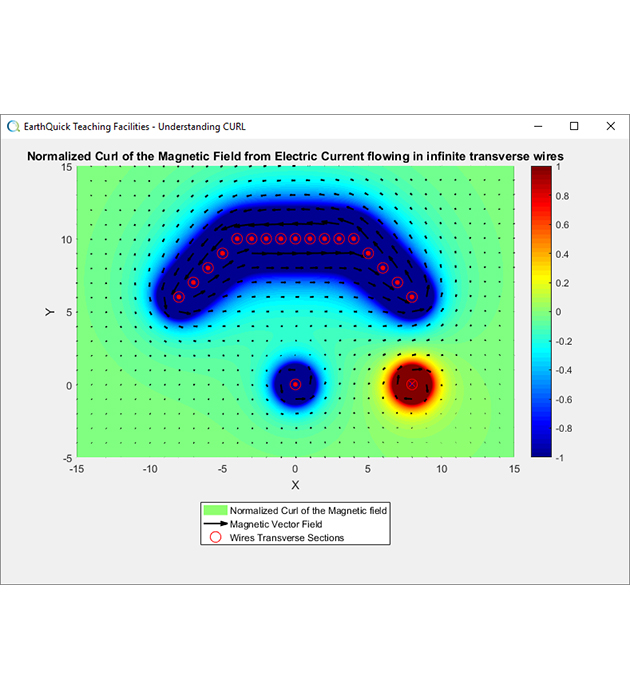
Linear operators in action - Curl of the magnetic field
Step 6/6
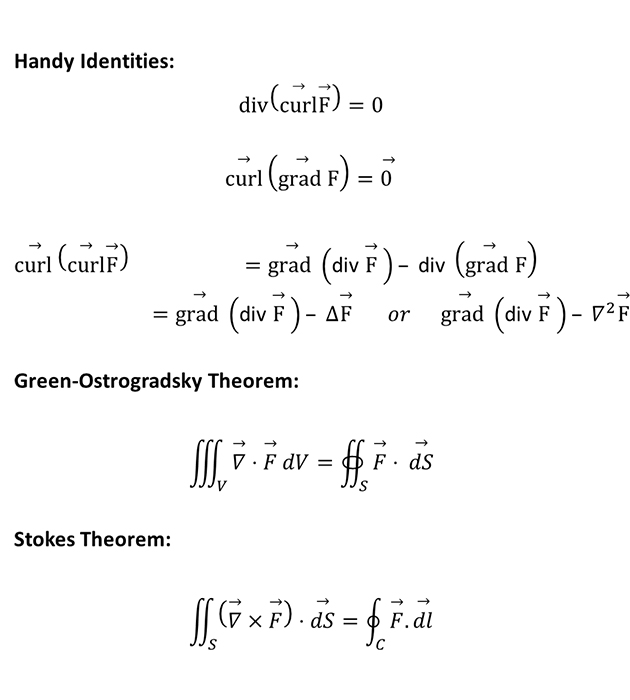
Handy Identities and Theorems