-
Step 1: Instantaneous Frequency fundamentals.
The opposite panel gives an overview of the attribute characteristics.
-
Step 2: Before attribute computation - Reflected amplitudes.
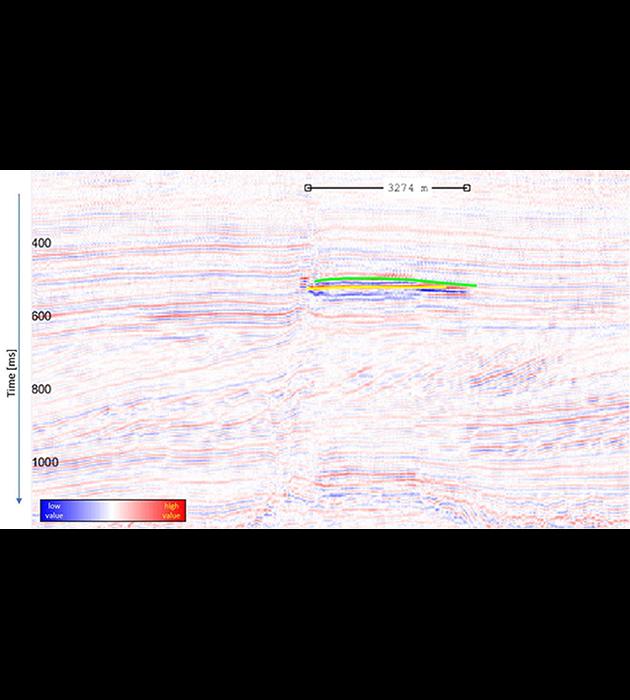
The seismic section is the inline 230, extracted from post-stack time migrated 3D seismic data (Netherlands, F3 Block). After Guo (2014), Top and Base of a shallow Gas reservoir have been picked on seismic reflected amplitudes data. Green picking stands for the Top reservoir (dim spot), whilst yellow picking corresponds the base of the Gas accumulation (flat spot). To deal with concrete matters, results from published works have been used to build an example of "Low-frequency shadows" (after Chopra et al, 2000).
-
Step 3: With the Instantaneous Frequency attribute.
Same Top and Base of a shallow Gas reservoir have been reported on Instantaneous Frequency attribute. Same inline is displayed.
Below reservoir low-frequency shadows are observed as expected. Additionally, above the reservoir lower frequency content may be due to gas leakage/chimney.
References::
- Chopra, S. and Marfurt K. J. [2007] Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization, Society of Exploration Geophysicists and European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, 138-144.
- Guo, Qiang, "TUNING, AVO, AND FLAT-SPOT EFFECTS IN A SEISMIC ANALYSIS OF NORTH SEA BLOCK F3", Master's Thesis, Michigan Technological University, 2014.
- Schroot, B. M., and R. T. E. Schuttenhelm., 2003, Expressions of shallow gas in the Netherlands North Sea: Netherlands Journal of Geosciences, 82(1): 91-106.
Acknowledgements:
The example is made of Post-stack time migrated 3D seismic data (Netherlands, F3 Block) provided by dGB Earth Sciences through OpendTect share seismic data repository. Netherlands Government is kindly acknowledged for making data public if dedicated to academic purposes.